Chiara Pancotti and Matteo Pedralli contributed to a ZEW’s discussion paper titled “The Recovery and Resilience Facility: Key Innovations and the Interplay With Cohesion Policy”, which originates from the study conducted for DG ECFIN “Supporting the Mid-term Evaluation of the Recovery and Resilience Facility” in 2023-2024.
With the aim of contributing to the ongoing discussions on the future of the post-2027 Cohesion Policy, the paper delves into the functioning of the Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF). It examines the interplay between the RRF and CP, illustrating their respective governance structures, the key strengths of the RRF, the main obstacles to its implementation, and the interaction between the two instruments. The chapter concludes that the RRF can provide at least two sources of inspiration for the future of CP and EU public investment policies: the performance-based payment mechanism and the link between reforms and investments.
We have recently completed a new study on Open Strategic Autonomy (OSA) and its impact on SMEs in the European economy, conducted for the European Commission’s DG GROW in partnership with IDEA Consult, PPMI, and LSE Consulting.
This study analysed the implications of OSA for SMEs, the extent and manner in which SMEs are involved in strategic industries and technologies, and how their involvement could be improved to secure the success of the OSA goals.
OSA is becoming a pervasive concept in many EU policies, including trade industrial, defence and security and research policies. While OSA initiatives often focus on large companies and “national champions” with the capacity to compete globally, the participation of SMEs can help build more resilient and diversified supply chains.
Key highlights include:
The results of this study have been incorporated into the newly published Annual Report on European SMEs 2023/2024.
Along with the final reports and annexes, we have also produced an infographic summarising the study’s main messages and action plan for an OSA that leverages SME capabilities to ensure more successful and sustainable EU policies.
? Full study SMEs and Open Strategic Autonomy
Contact us if you want to know more or discuss the study’s findings with the project team.
Jessica Catalano and Valentina Morretta have authored a chapter titled “The Socio-Economic Benefits of Earth Observation (EO): Insights from the End Users of EO Services and Applications in Italy,” which is part of the newly published, open-access OECD publication “The Economics of Space Sustainability: Delivering Economic Evidence to Guide Government Action”.
Earth observation (EO) is a rapidly evolving field within the space economy, contributing significantly to our understanding and management of Earth’s natural and societal aspects. Despite EO’s increasing importance, the literature provides limited evidence regarding its socio-economic benefits for end users. The chapter addresses this gap by presenting findings from a survey distributed to end users of EO services in Italy, a nation actively engaged in the space economy’s entire value chain.
Their research uncovers the various socio-economic advantages derived from using EO data, providing insights into this strategic domain. The chapter highlights the importance of EO services in areas such as weather monitoring, disaster management, and environmental protection, demonstrating their critical role in enhancing societal well-being and economic development.
The book “The Economics of Space Sustainability” presents the latest findings from the OECD project on the economics of space sustainability. It evaluates the societal value of space infrastructure and discusses methods for mitigating space debris, including case studies from Italy, Japan, and Korea.
As OECD publications, the chapter and the book are available for free through open access.
Catalano, G. and V. Morretta (2024), “The socio-economic benefits of earth observation (EO): Insights from the end users of EO services and applications in Italy”, in The Economics of Space Sustainability: Delivering Economic Evidence to Guide Government Action, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/f2558ff5-en.
OECD (2024), The Economics of Space Sustainability: Delivering Economic Evidence to Guide Government Action, OECD
Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/b2257346-en.
Photo credits: Cover © Frame Stock Footage/shutterstock.com.
According to CSIL (Furniture retailing in Europe 2024 report), the European retail furniture market is worth EUR 165 billion. The market exhibited robust growth in 2021, followed by a deceleration in 2022 and a contraction in 2023 (-3.5%).
In 2023, influenced by the natural shift in demand post-pandemic, the rising cost of living has intensified pressure on consumer spending, particularly for big-ticket items such as furniture. However, despite ongoing uncertainties, the newfound significance of the home, stemming from the pandemic, is anticipated to drive new demand, with furniture extending beyond its practical functionality.
Europe continues to play an important role in the global furniture market, being the third-largest one in the world after Asia Pacific and North America. With more than 230 million households and one of the highest per capita consumption levels, Europe accounts for more than a quarter of the global world furniture market. Its influence is also discernible in production value and extends to market dynamics and international trade values.
Europe retains its status as a key hub in world trade, underscoring its continuing importance in terms of market size and overall impact on the global furniture landscape. A significant proportion of the current demand in Europe is met by EU production, making up 80% of the total consumption, while the remaining portion is sourced through imports from other countries.
Most furniture manufacturers surveyed by CSIL during 2023 claimed that they increasingly shorten their supply chains by being more local (at the country or regional level). Within Europe, Portugal, Italy, and Spain are the main beneficiaries of this perspective. The relocation is driven by various reasons, including shortening the time to market. Still, business sustainability, liquidity, and supply security have emerged as key issues that international events intensify.
Read the full article on World Furniture Online
The XI edition of the Milan Summer School in Cost-Benefit Analysis will be held in Milan from 9 to 13 September 2024.
The Summer School offers an intensive and interactive learning experience focused on CBA as a tool supporting the decision-making process of public investments. It allows participants to acquire a solid background in different aspects:
Participants may join the format that best suits their needs and availability:
The Summer School’s lecturers are experts—academics and consultants—with longstanding experience designing, implementing, and reviewing CBA of infrastructure projects. Among them are experts involved in preparing the European Commission’s Guide to Cost-Benefit Analysis of Investment Projects and the Economic Appraisal Vademecum 2021-2027.
Previous participants said:
CSIL is a partner of the Horizon PathOS project, which aims to identify the key impacts and different paths of open science across academia, economy and society.
PathOS serves as a comprehensive resource hub, offering insights into the effects of Open Science with the aim of facilitating the development of effective policies. To this end, the team developed and curated essential tools, such as an Open Science Indicator Handbook, alongside a curated Zotero library that tracks the multifaceted impacts of Open Science literature.
Continuously evolving, PathOS also features a collection of Open Science Stories, Tools, and Data for impact measurement, frameworks for assessing Open Science impact pathways and conducting cost-benefit analysis, as well as a wealth of training resources and materials.
For more information about CSIL’s contribution, see

We are thrilled to announce the release of the study titled “Supporting the Mid-term Evaluation of the Recovery and Resilience Facility,” conducted by Ecorys, CSIL, CEPS, NIESR, and Wavestone between March and October 2023. The study, commissioned by the European Commission’s Directorate General Economic and Financial Affairs, aims to provide an objective and independent assessment of the effectiveness, efficiency, relevance, coherence, and EU-added value of the Recovery and Resilience Facility. The supporting study feeds into the EC’s mid-term evaluation report. Moreover, the study also provides useful background evidence and lessons learned for discussions on possible future performance-based instruments in the post-2027 Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF).
To achieve the objectives of the evaluation, various methodologies were employed, including an extensive literature review, the analysis of the RRF scoreboard data, surveys targeting key national stakeholders, targeted interviews, eight case studies focusing on specific policy areas related to the RRF’s pillars and cross-cutting aspects, workshops, analysis of costs and benefits, macroeconomic modelling, and public consultation. CSIL experts have been specifically involved in the surveys, the interviews, the case study on the interaction between EU Cohesion Policy and the RRF, and the analysis of cost and benefits.
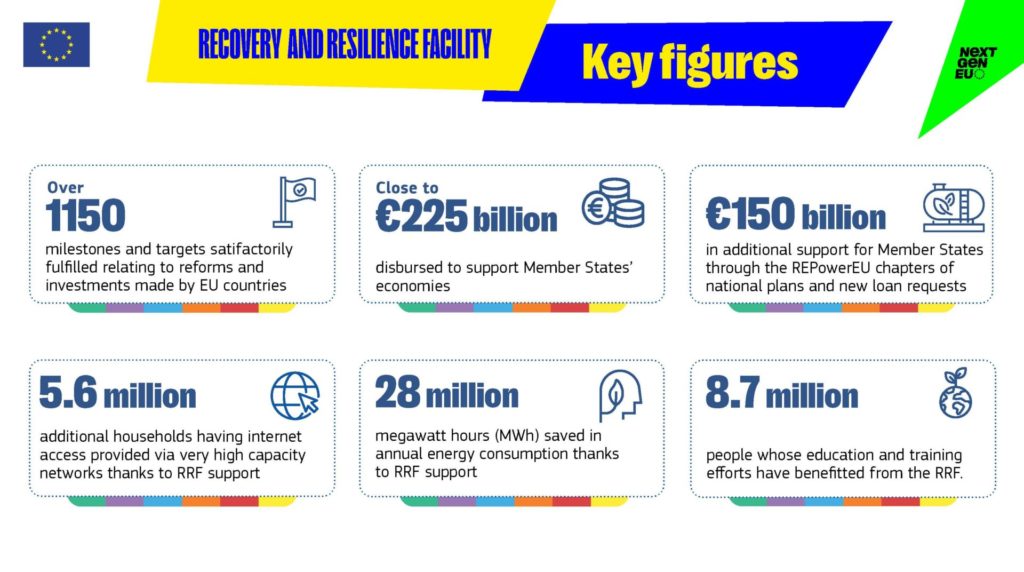
The RRF, with its unprecedented financial size and nature, has emerged as a cornerstone for supporting reforms and investments across the 27 Member States. With a significant amount of financial resources (up to €723.8 billion in total), the RRF has provided crucial support to increase resilience in response to the COVID-19 crisis and helped address longstanding challenges hampering growth and socio-economic development.
The performance-based approach is certainly the main innovation of the RRF, together with the large issuance of common EU debt and the focus on a combination of reforms and investments.
As of mid-2023, 31% of the overall amount of planned grants and loans has been disbursed under the RRF. Nevertheless, the pace of financial progress presents a significant risk of delays compared to indicative planning, attributed to various factors, including revisions of plans, difficulties in meeting milestones and targets, changes in government priorities, administrative capacity issues, and external factors such as geopolitical events and economic challenges.
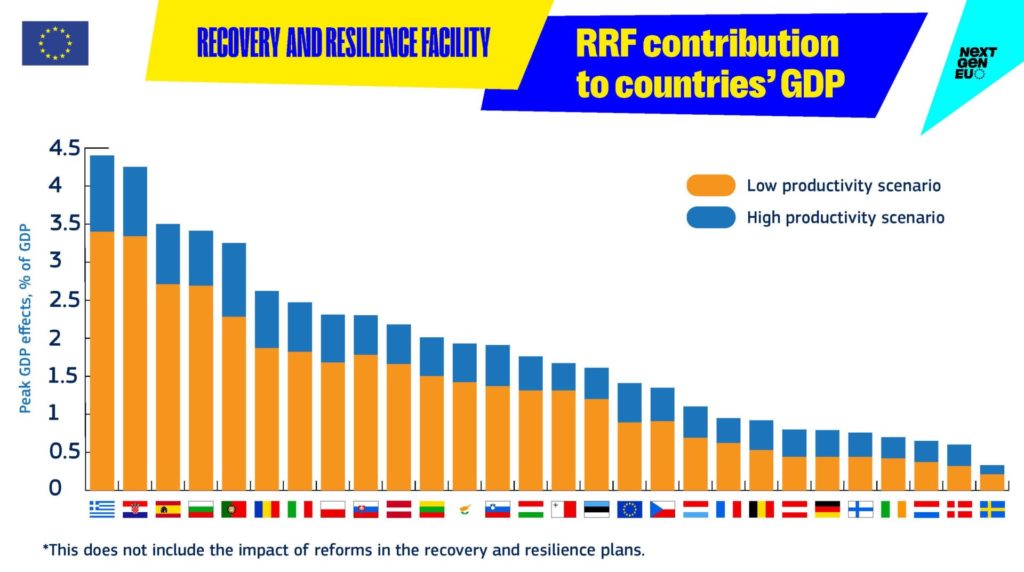
The general conclusion of the study is that the RRF provided a macro-relevant common and synchronised EU response to support Member States’ recovery after the COVID-19 pandemic and the energy crisis. The evaluation findings show that the RRF has triggered the implementation of major and long-awaited reforms across a wide range of policy areas, increased EU GDP, lowered EU unemployment, and helped avoid financial fragmentation. Nevertheless, the risks associated with the implementation of the RRF will need to be closely monitored in the coming years.
Learn more about the RRF’s estimated contribution to the EU countries’ GDP and project examples across all six policy pillars in the infographics below:






For more information, see:
CSIL has recently released World Furniture Magazine #01, the inaugural edition of CSIL’s new digital quarterly publication. Themed on the latest updates from the Furniture and Lighting industry, the magazine provides economic insights and market analysis.
Some highlights include:
World Furniture Outlook 2024: According to CSIL, in 2024, a decline in consumer confidence and weakened furniture demand are expected. Globally, furniture consumption is forecasted to experience a slight decrease in real terms in 2024, with a potential resume in 2025.
India emerges as the fourth-largest furniture market globally, soaring from 10th place a decade ago to a value of approximately US$ 19 billion in 2023. With robust economic growth in 2023 and anticipated continuity in 2024, India’s furniture sector remains a force to reckon with.
Market intelligence: With a value of around EUR 110 billion, the European furniture market accounts for over one-quarter of the global one. The kitchen furniture industry in 2023 reached a total production value of US$ 62 billion, around 13% of total world furniture output.
Focus on Sustainability: From European furniture companies embracing the green transition to initiatives driving mattress traceability, explore the latest developments in sustainability across the industry.
From trend talks to the impact of high inflation on European SMEs, the magazine presents additional insights and contributions enriching industry understanding.
Download World Furniture Magazine #01!

Our latest study, “Access to Equity Financing for European Defence SMEs,” sheds light on the implications of restricted financial access for defence SMEs in the EU. Securing funds is vital in the current geopolitical context. The resurgence of war in Europe and rising tensions have created a new urgency for the EU to better address existing and foreseeable security and defence challenges.
Key findings from our study reveal that 40% of SMEs find access to finance challenging. Moreover, a considerable share of defence SMEs refrained from pursuing either bank loans (44% of SMEs) or equity financing (68%) during 2021-2022. Financing is crucial for EU defence sector companies to offset years of underinvestment. Our study identifies an average equity financing gap of EUR 2 billion and a debt financing gap of EUR 1 to 2 billion for SMEs and Midcaps in the defence sector.
This limited access can be attributed to the unique characteristics of the defence industry, including its dependence on public procurement, stringent regulations, and the need for cautious approaches in military technology investments. Additionally, ethical considerations and a too rigid interpretation of ESG criteria contribute to the challenge.
While increased defence spending, technological advancements, and the dual-use nature of technologies attract private investor interest in the defence and dual-use technology sector, it falls short of meeting current needs. Public sector involvement, through specific programs and national promotional banks, plays a crucial role in signalling to private investors and mitigating investment risks.
A new CSIL working paper authored by Emanuela Sirtori shows how community detection analysis of a network of patent technology codes (IPC) can be used to classify a large and sparse patent database in a fully automated and unsupervised way. The research aligns with the increasing demand for efficient methods to identify meaningful technological domains that can inform the study of technologies and their evolution.
Light Emitting Diode (LED) has been selected as a test-bed of the methodology. As a multi-purpose technology, LED evolved for decades, spanning several technology fields, before finding mass application in the general lighting industry. The analysis has been conducted over the largest database of patents related to LED ever used in the literature, covering over 400 thousand patent documents filed in 77 patent offices in the world between 1962 and 2018. VOS and Louvain community detection algorithms have been applied to find the technology domains around which the patent activity concentrated across the long and multi-directional historical evolution of LED.
Results have been compared with other studies and approaches in order to highlight the advantages of the proposed methodology. IPC-based community detection proves particularly useful in classifying other
technologies characterised by a meandering evolutionary process across several domains. It does not require particularly advanced data science skills and allows the flexibility of choosing the level of granularity in the classification by adjusting the resolution parameter.
Sirtori E (2023), “Identification of multiple technology domains of LED through IPC community analysis”, Working Papers 2023/02, CSIL.